Image ID: 221
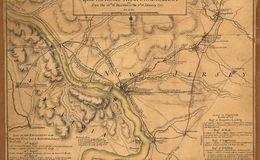
Trenton, NJ- Outpost of 1400 Hessians at end of the long line stretching from New York City.
An American camp in Pennsylvania, centering around Newtown.
Washington crosses the Delaware River at McConkey's ferry, night of Dec 25-26, 1776.
One American column under Ten. Washington and Greene approach Trenton along Pennington Road.
The other American column under General Sullivan approach from the River Road.
The two American columns converge on the Hessians simultaneously and rout the garrison in a battle lasting less than an hour.
A week later, Washington gained another victory at Princeton, NJ. These two military successes saved the cause of American Independence. Washington showed battlefield genius. He had, indeed, made mistakes that year, but he learned. No matter how desperate the campaign had been, he responded with an iron will, bravery and determination.No one else could have done what General George Washington did in that fateful campaign of 1776.
Dots OFF
Dots ON




1777 Trenton Map

1776 Trenton